Crypto Mental Models (Hashing, Encryption, Keys)
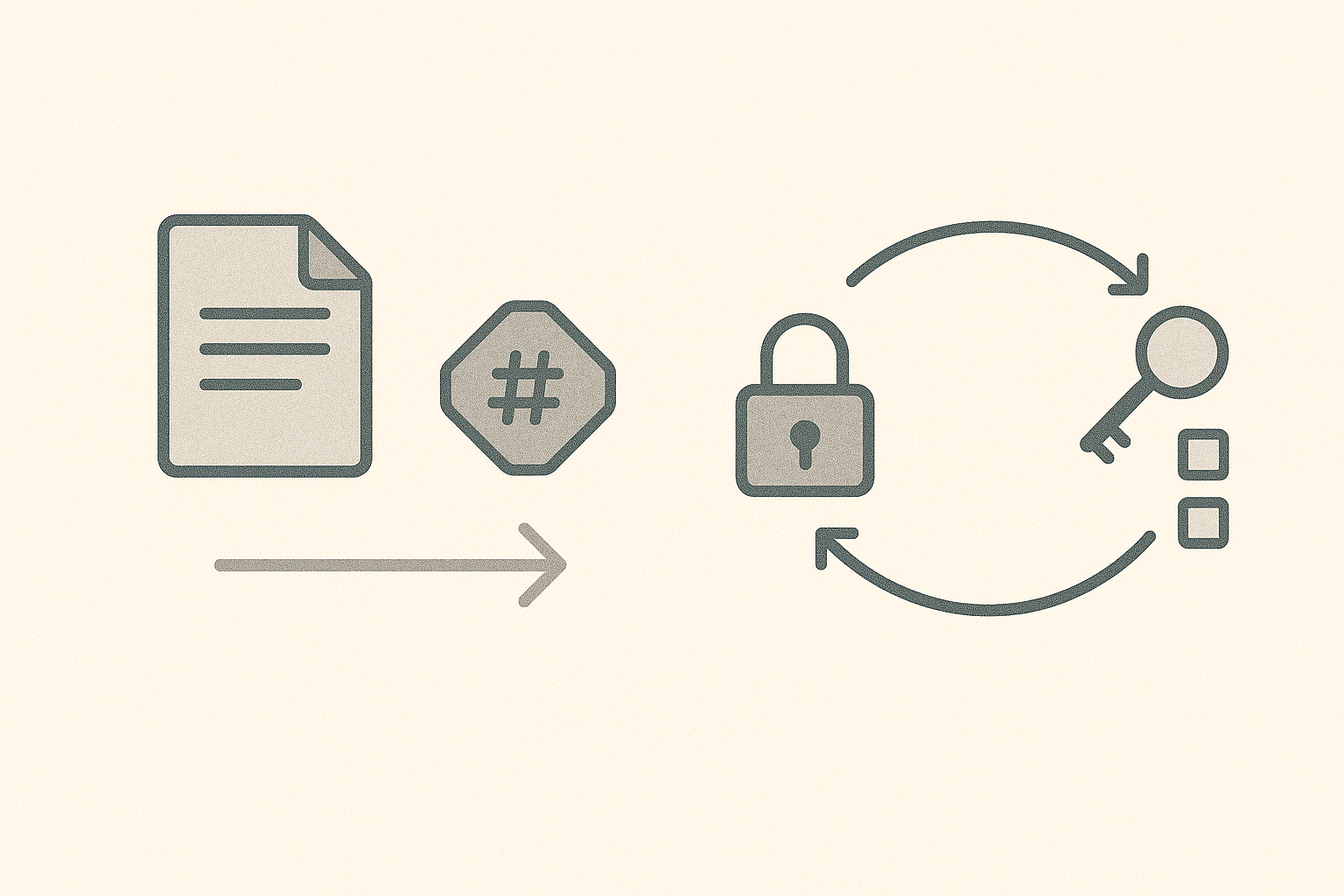
Hashing (one-way)
A hash turns data into a fixed-length value.
- Used to check integrity (did the file change?)
- Used in password storage (with proper methods)
Hashing is one-way: you cannot “decrypt” a hash back into the original.
Encryption (two-way)
Encryption transforms data using a key. If you have the key, you can decrypt.
Symmetric vs asymmetric (high level)
- Symmetric: same key encrypts and decrypts (fast)
- Asymmetric: public/private keys (useful for identity and secure key exchange)
TLS (what HTTPS uses)
TLS protects data in transit (between your browser and the server). It does not guarantee the website is honest—it guarantees you are connected securely to that site.
Quick check (2 minutes)
- Which is one-way: hashing or encryption?
- What does TLS protect: data at rest, data in transit, or both?