Web Basics (HTTP/S) for Cyber
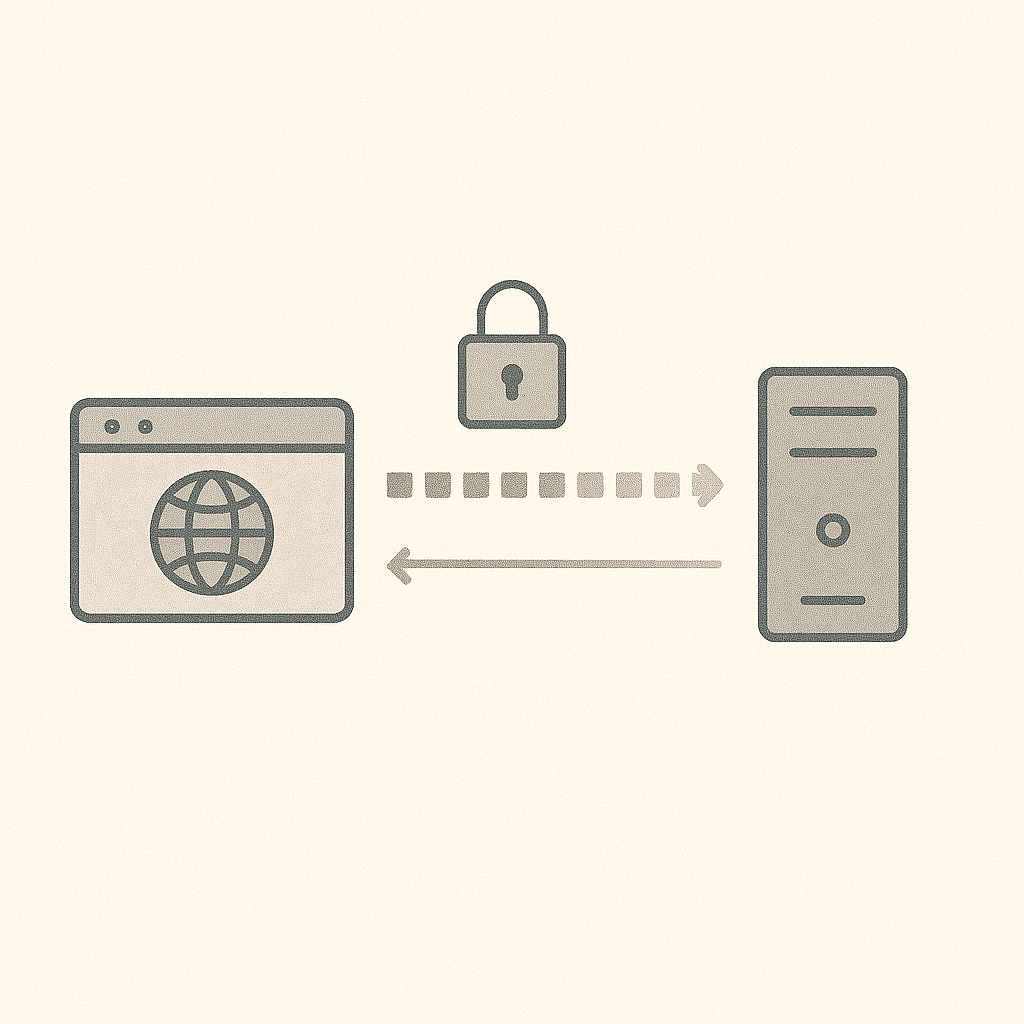
What happens when you visit a website
- Your device resolves a name (DNS)
- Your browser connects to a server
- The browser requests a page (HTTP)
- The server responds with content
HTTP vs HTTPS
- HTTP: sends data in plain text (not safe on untrusted networks)
- HTTPS: encrypts data in transit and validates the server’s identity (certificate)
Cookies and sessions
- A cookie is small data stored by your browser
- A session is how a site remembers you are logged in
If someone steals your session cookie, they may not need your password.
Practice (5 minutes)
Write one reason HTTPS matters:
- For confidentiality:
- For integrity:
- For identity: